이벤트 전파
이벤트 전파 흐름
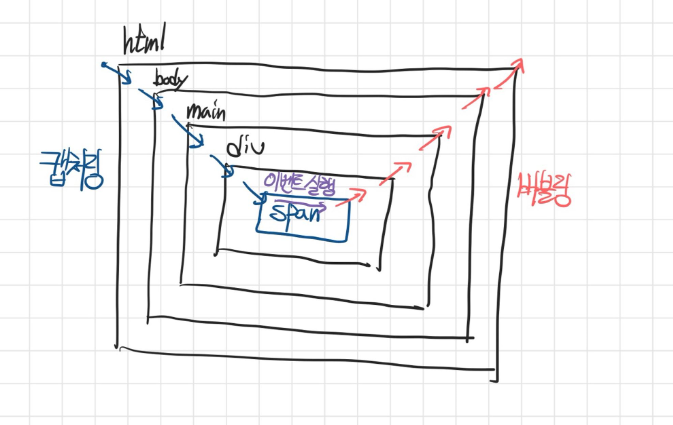
html > body > main > div > span으로 구성된 HTML 문서에서span에 클릭 이벤트가 발생했다고 가정하자.- 이때 클릭 이벤트도
html > body > main > div > span순으로 루트부터 타겟 요소까지 타고 내려가는 형식으로 전파된다.- 이 이벤트 전파 흐름을 이벤트 캡쳐링(capturing)이라 한다.
- target 요소에 도달한 이벤트는 실행 후 역순으로
span > div > main > body > html으로 전파된다.- 이 이벤트 전파 흐름을 이벤트 버블링(bubbling)이라 한다.
addEventListener의 이벤트 전파
자바스크립트에서는 DOM 요소에 eventListener를 등록하여 이벤트를 캐치하는데, 이 때 기본값은 버블링이다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css" /> </head> <body> Body <main> Main <div>Div<span>Span</span></div> </main> <script> const body = document.querySelector("body"); const main = document.querySelector("main"); const div = document.querySelector("div"); const span = document.querySelector("span"); body.addEventListener("click", function () { console.log("body"); }); main.addEventListener("click", function () { console.log("main"); }); div.addEventListener("click", function () { console.log("div"); }); span.addEventListener("click", function () { console.log("span"); }); </script> </body> </html>
addEventListener의 세번째 파라미터로true를 전달하면 캡처링으로 동작하게 된다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css" /> </head> <body> Body <main> Main <div>Div<span>Span</span></div> </main> <script> const body = document.querySelector("body"); const main = document.querySelector("main"); const div = document.querySelector("div"); const span = document.querySelector("span"); body.addEventListener( "click", function () { console.log("body"); }, true ); main.addEventListener( "click", function () { console.log("main"); }, true ); div.addEventListener( "click", function () { console.log("div"); }, true ); span.addEventListener( "click", function () { console.log("span"); }, true ); </script> </body> </html>
- 캡처링 순서에 따라
body > main > div > span순서로 이벤트가 전파되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
- 캡처링 순서에 따라
event.eventPhase
이벤트 리스너가 전달하는
event객체에는eventPhase라는 속성이 존재한다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>Document</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./style.css" /> </head> <body> Body <main> Main <div>Div<span>Span</span></div> </main> <script> const body = document.querySelector("body"); const main = document.querySelector("main"); const div = document.querySelector("div"); const span = document.querySelector("span"); body.addEventListener( "click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "body"); }, true ); main.addEventListener( "click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "main"); }, true ); div.addEventListener( "click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "div"); }, true ); span.addEventListener( "click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "span"); }, true ); body.addEventListener("click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "body"); }); main.addEventListener("click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "main"); }); div.addEventListener("click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "div"); }); span.addEventListener("click", function (event) { console.log("[" + event.eventPhase + "]" + "span"); }); </script> </body> </html>
- 1 : 캡쳐링 과정 (루트 요소로부터 타겟 요소로 전파중인 상태)
- 2 : 실행 과정 (타겟 요소에 도착한 상태)
- 3 : 버블링 과정 (타겟 요소로부터 루트 요소로 전파중인 상태)
이벤트 전파 방지
stopPropagation()
- 개발 과정 중 이벤트 전파를 막아야하는 상황이라면
event.stopPropagation()메서드를 통해 이벤트 전파를 막을 수 있다. - 설사 타겟 요소에 도착하지 못한 상태더라도 중간에
event.stopPropagation()가 호출되면 이벤트 전파가 멈춰버린다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.